SKIN PROTECTION GUIDE

WHATS THE RISK?
As we all know, intensity of UV radiation in New Zealand is very high, especially in summer.
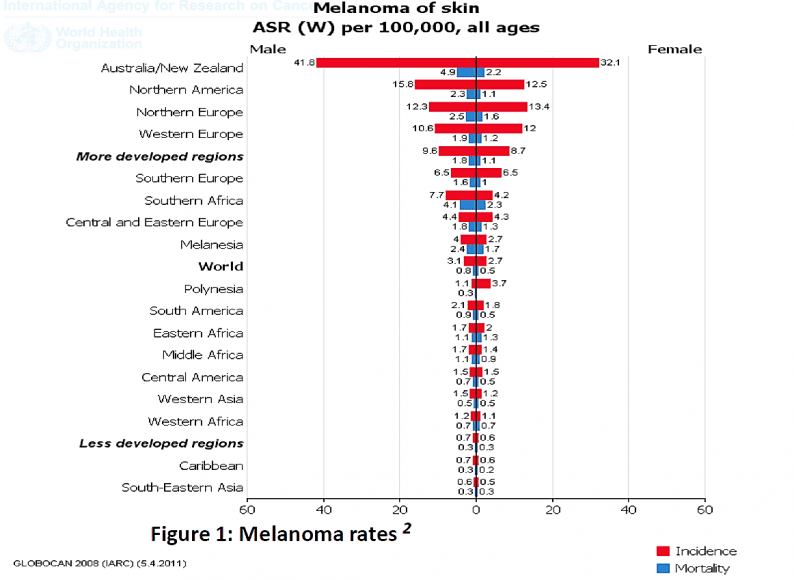
Our skin cancer rates are the highest in the world and skin cancer is by far New Zealand’s most common cancer.
There are about 82,000 new cases of skin cancers each year, compared to a total of 16 000 for all other types of cancer. The incidence of melanoma in New Zealand is the highest in the world—higher than Australia and around four times higher than in Canada, the US or the UK.
If you are an employer and your staff are working outside, especially during summer months, you need an appropriate UV safety program, which includes supplying staff with an effective sunscreen. WorkSafe NZ’s webpage Protecting workers from solar UV radiation says:
“Personal protection is an important component in any plan to control exposure to solar radiation. An effective plan will usually involve protective clothing, hat and a sunscreen. Complete reliance should not be placed on any one form of protection. Sunscreen should be applied to all uncovered skin.”
ESKO SunGard is laboratory tested in Australia to validate its SPF50 rating and effectiveness against UVA radiation. Download our Sungard MSDS Sheet
What is SPF?
The SPF (Sun Protection Factor) number is calculated by simulating in-the-field usage conditions in a laboratory. This involves exposing the skin of human volunteers to various amounts of simulated sunlight before and after the application of a standard amount of sunscreen.
The SPF of a sunscreen is derived by taking the time it takes the trial participant to burn with a sunscreen and dividing it by the time taken for the participant to burn without a sunscreen. For example, if the trial participant burns in 300 minutes with a sunscreen and in 10 minutes without a sunscreen, this is calculated as 300/10 = 30; equivalent to an SPF of 30.
ESKO SunGard sunscreen is laboratory tested to an SPF rating of 50 under the AS/NZS sunscreen standards.
Healthcare providers recommend:
- Use a sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or greater on all exposed skin.
- Use a sunscreen like ESKO SunGard that protects against both UVA and UVB radiation.
- You may need a higher SPF if you are fair-skinned, if you will be in the sun for a long time, or if UV exposure is intense (eg, at the beach or skiing).
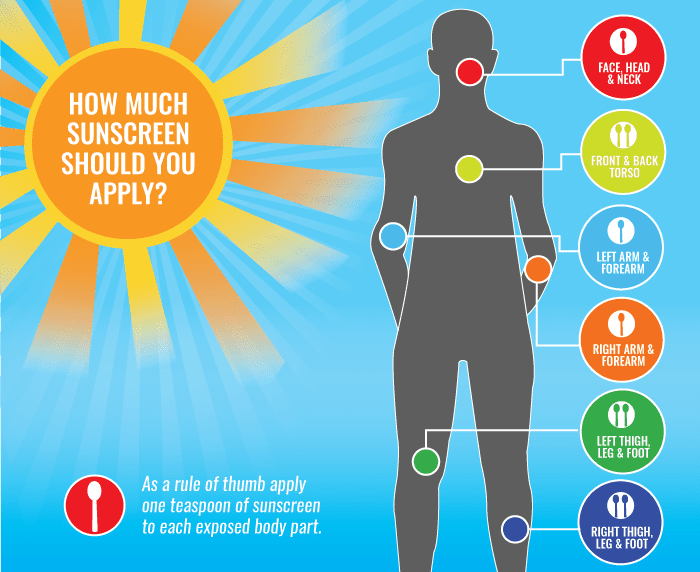
- Apply sunscreen generously to all exposed skin 15 to 30 minutes before exposure and remember to apply to your ears. Approximately two tablespoons of sunscreen (about a shot glass full) is needed to cover an adult’s arms, legs, neck, and face.
- Reapply sunscreen after sweating, rubbing the skin, swimming or drying off with a towel. Reapply every two to three hours.
- Protect your lips with lip balm.


Sunscreens need to be applied liberally to achieve the SPF protection claimed on the label.

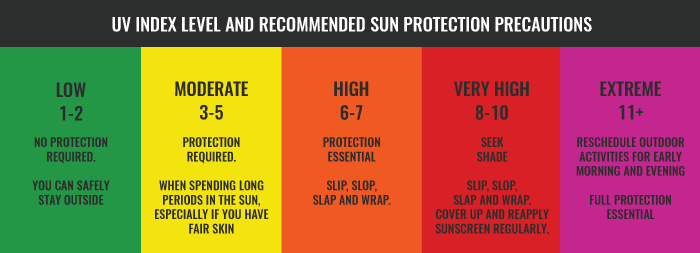
What is the UV Index (UVI)?
The UV index is a standard measurement of sunburn-causing UV intensity. The scale is open-ended, but a UV index of greater than 10 is extreme and a UV index of less than 3 is low.

New Zealand's Risk FACTOR is greAter than anywhere else in the world:

More information
Click on the links below for further information:’
Worksafe’s guide to Protecting Workers from Solar UV Radiation
Sunsmart’s webpage on Managing and Monitoring Workplace UV Exposure
UVI forecast for specific NZ and Pacific sites
Other helpful NZ-specific resources at sunsmart.org.nz
Relevant standards:
- AS/NZS 2604:2012 Sunscreen products – Evaluation and classification
- Australian regulatory guidelines for sunscreens (ARGS)